Filters
Streamline your data discovery by applying tailored filters to efficiently navigate and manage resources in Secoda.
Overview
Filters are powerful tools in Secoda that enhance your ability to efficiently explore and access metadata. This guide explains how to set up and effectively use filters in both the Catalog and Search functions.
Filtering your Search
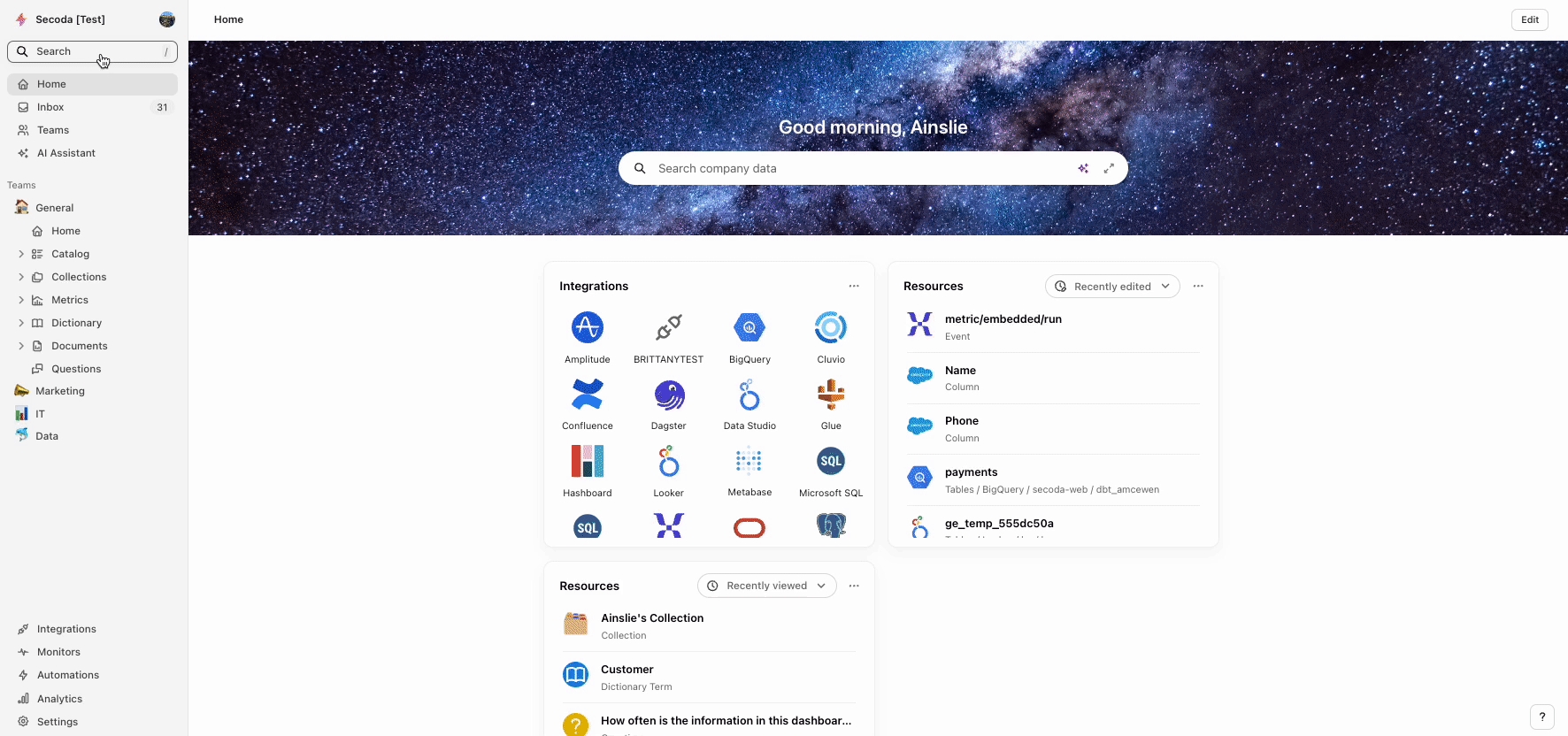
Use Secoda's Search function to apply filters and narrow down your results. This is particularly useful when searching for specific data characteristics across your entire database.
Filter categories
In Secoda, you can apply filters based on the following categories:
Resource characteristics
Type, Integration, Related, Quality
Metadata properties
Title, Description, Tags, Status, Priority, Published, Collections, Owners, Governance, Verification, Teams
Temporal filters
Created time, Updated time, Externally updated time
Source filters
Metadata source, Group, Schema, Database, Table
Build filters with operators
Once you add a filter, refine it with operators. The filter type itself cannot be changed, but you can modify other components of the filter to tweak your query. For example, a filter for "Owner is [email protected]" can be adjusted as follows:
Clicking on "is" allows you to change the operator to "is not" or "is not set".
Clicking on "[email protected]" will display a selectable list to modify the owner.
We support the following operators in Secoda, which will show up depending on the type of filter and selections:
is, is not, and is not set when one option is included in the filter.
is any of, is not and is not set when multiple options are included in the filter.
is on or before or after for date-related filters.
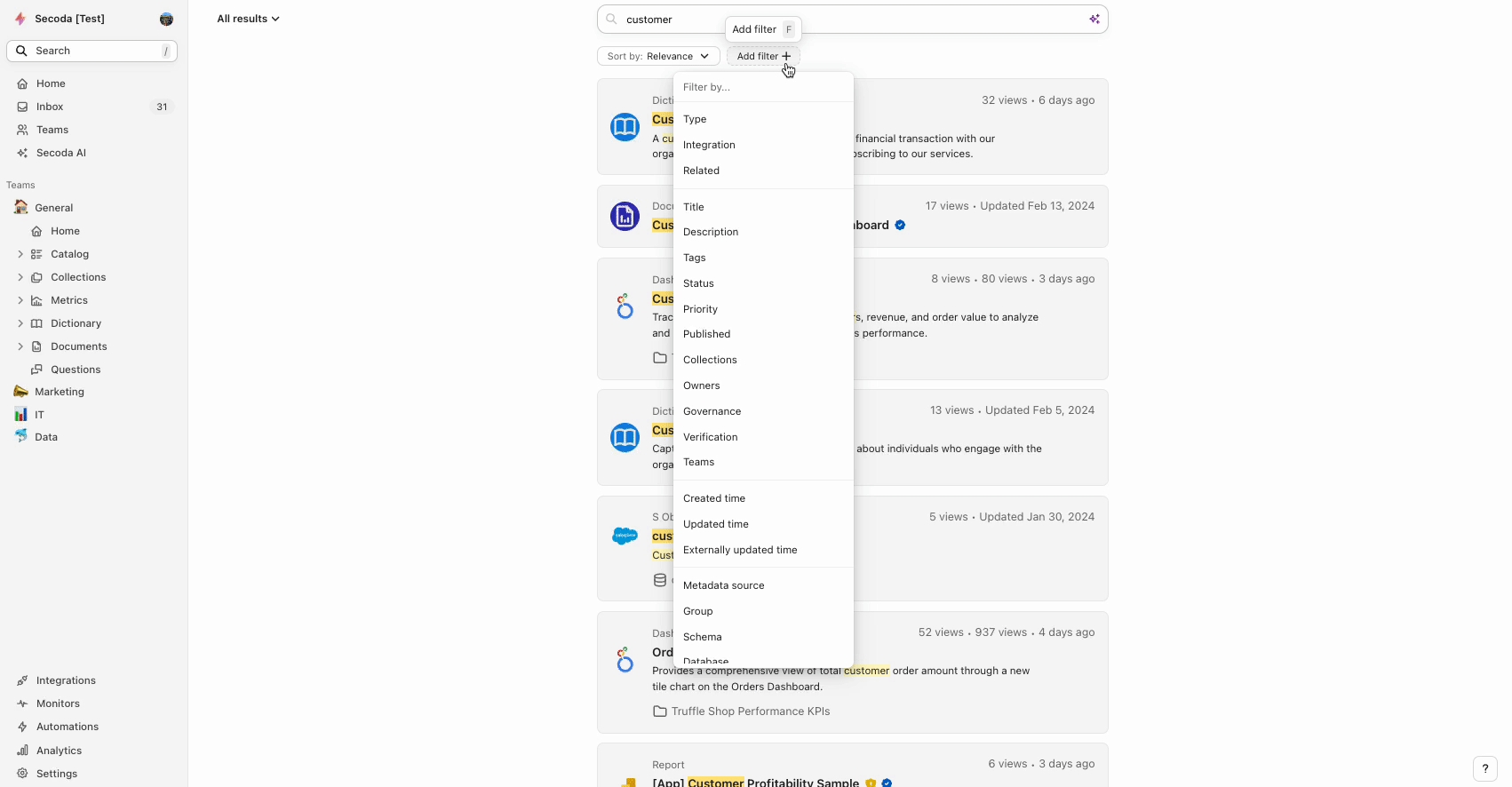
AI Filters
With AI Filters, you can filter your data using plain language, making it easier to find exactly what you need. Simply select "AI Filters" and type out what you'd like to see. This limits the amount of clicking and searching, saving you valuable time.
Create views
Consider saving your filters with Views to streamline your workflow, particularly if you frequently revisit specific datasets. Saved views can be quickly accessed, reducing the time spent reapplying the same filters.
Advanced Filtering Capabilities
Nested Search in Filters: We've added nested search capabilities to filters. For instance, you can directly search for a user's name without having to navigate through "Owners" first. This makes it quicker and more intuitive to find specific entries.
Keyboard Shortcuts for Filters: To improve efficiency, you can now use the keyboard shortcut '(f)' to open filters and navigate through them with ease.
Combining Filters: Combine multiple filters for more precise data retrieval. For instance, you can combine filters for 'Owners' and 'Status' to track recent changes by specific team members.
Using Boolean Operators: Incorporate operators such as IS, IS NOT for complex searches that require a combination of conditions.
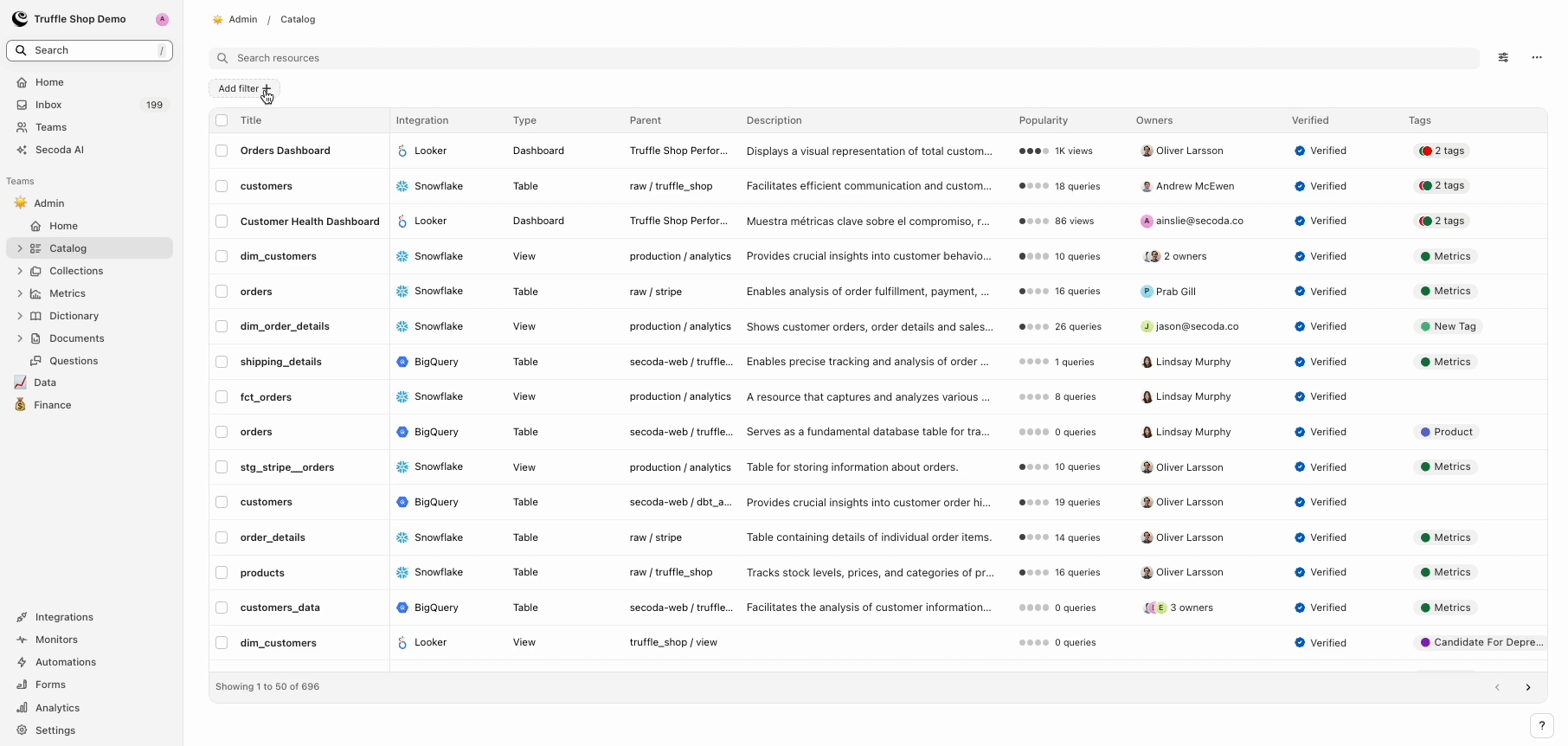
Applying Filters in Catalog
To utilize the advanced filtering capabilities:
Access Filters:
Go to any section where Filters can be applied, such as the Catalog, Collections, Metrics, Dictionary, Documents, or Questions. For this example, we'll use the Catalog.
Click 'Add filter' above the table and begin typing to add or adjust filters without pre-selecting a category. Tip: You can type a value like "Snowflake" instead of having to click through "Integrations" + find and click Snowflake.
Alternatively, click on the column header that corresponds to the metadata type you want to filter (e.g., Integration, Type, Owners).
Accessing Filters
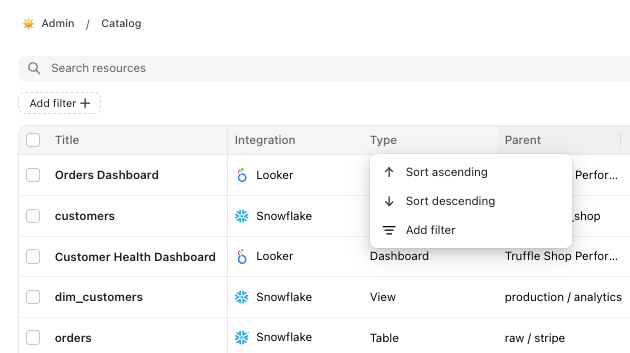
View Filtering Options:
Upon clicking the column header, a menu will appear offering several actions:
Sort Ascending/Descending: Order the metadata based on the selected column.
Add Filter: Customize your view by selecting specific criteria. This option is particularly useful for narrowing down your data visibility according to specific requirements.
Filtering Options
Apply Filters:
Select ‘Add Filter’ and choose the desired criteria from the list to refine your Catalog view.
Use Case: Filtering for Undocumented Resources
Filters can be used to identify resources that have not yet been documented in the workspace.
For example, to find resources without descriptions:
Click into the Catalog.
Navigate to the 'Description' metadata column.
Select 'Add filter' and 'is not set' to filter and display resources that lack descriptions.
Next you can apply descriptions in bulk using the AI description editor!
Last updated
Was this helpful?