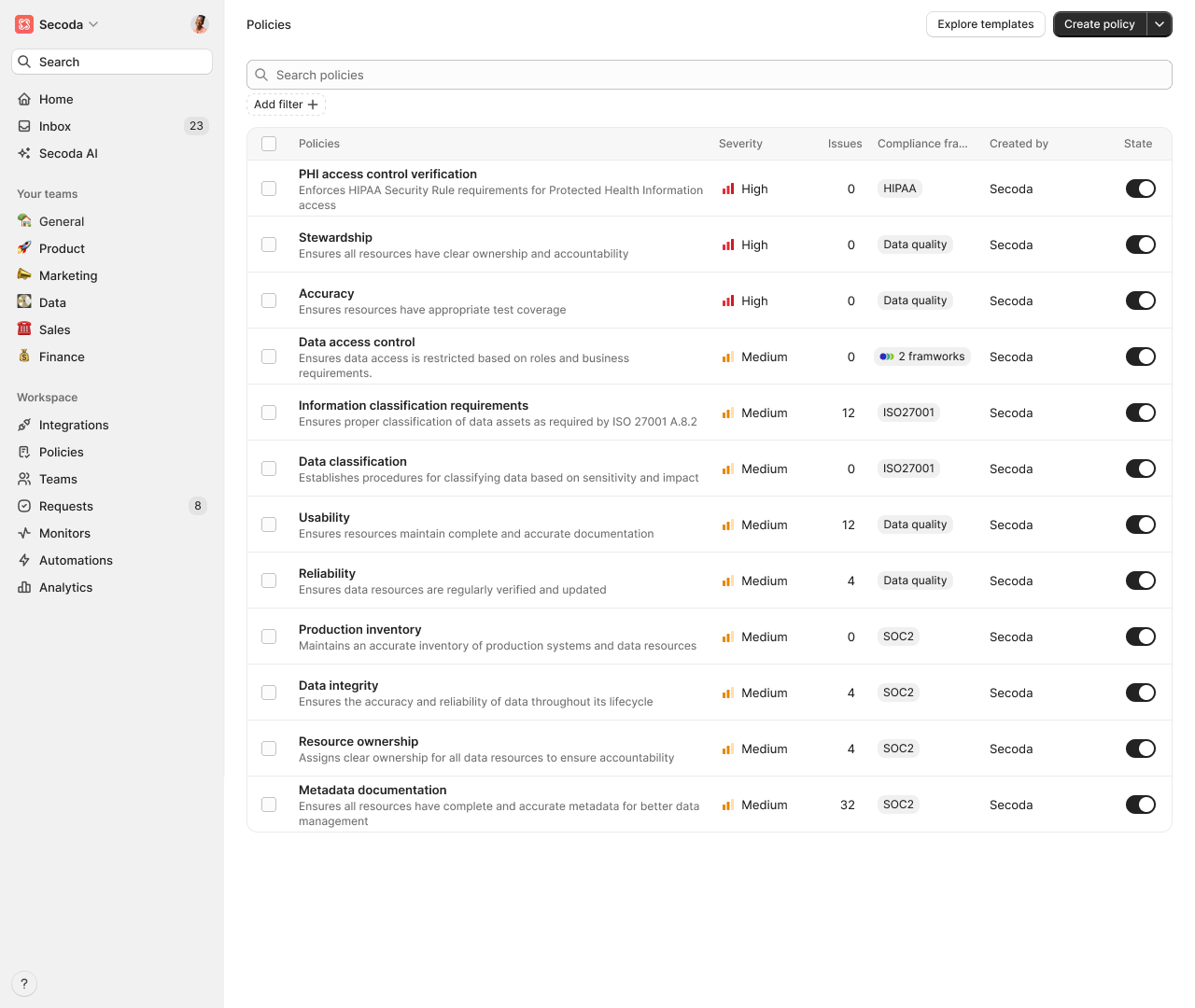
Policies
Policies enforce metadata standards across your workspace to ensure consistency, governance, and regulatory compliance.
Policies are available to customers on Premium plan. Interested in upgrade options? Click on the "Upgrade" button on the Policies page or reach out to the Customer team ([email protected]).
Policies in Secoda help organizations enforce data governance rules and maintain compliance across their data stack. With policies, teams can monitor, validate, and enforce data standards systematically.
Overview
Policies provide a structured way to:
Define and enforce data governance rules
Monitor compliance across your data resources
Track and remediate policy violations
Ensure data quality and security standards
Examples of Policies
Classification Tagging Ensures all resources are labeled with a sensitivity classification (e.g., PII, PHI, Confidential) to support data governance, access control, and compliance.
Retention Period Enforcement Requires that sensitive data assets (like PII or Confidential data) have a defined retention period to manage data lifecycle and meet regulatory requirements.
Encryption of Sensitive Data Mandates that tables containing sensitive or classified data are encrypted to protect against unauthorized access and align with security standards.
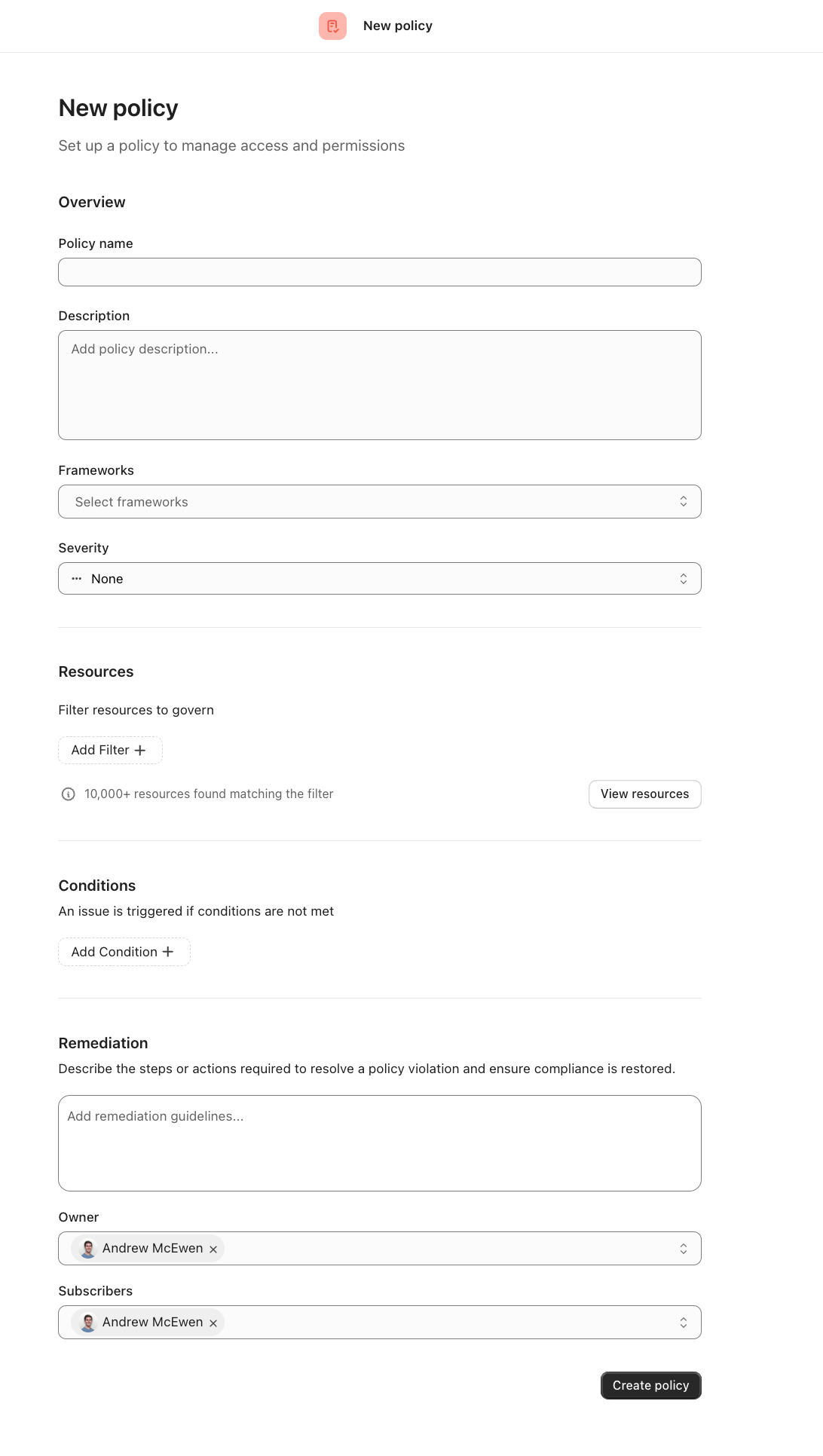
Creating Policies
To create a new policy:
Navigate to the Policies page
Click the "Add Policy" button
Define your policy details:
Name: Give your policy a descriptive name
Icon: Choose an icon to represent your policy (optional)
Description: Explain the purpose and requirements of your policy
Add filters for resources that are governed by the policy, e.g., Snowflake production table
Add conditions that must be met by the resources, e.g., Has owner
Managing Issues
Policy issues are flagged resources that do not meet the conditions defined in your policies. For example, if you have a policy requiring all tables with PII to be encrypted and a table is not encrypted, Secoda will surface that as a policy issue. These issues help you identify gaps in governance, security, or documentation so you can take corrective action.
How to Manage Policy Issues
View Issues Each policy has an "Issues" tab that lists all non-compliant resources. You can filter and sort these to focus on specific teams, systems, or classifications.
Investigate Context Click into an issue to view detailed metadata, related documentation, lineage, and ownership. This helps you understand why the issue exists and what needs to be fixed.
Remediate or Assign
Update metadata directly in Secoda (e.g., add a missing classification or owner).
Assign the issue to the correct stakeholder for follow-up.
Link the issue to external system such as Jira ticket or external task for tracking.
Mark as Resolved Once the resource complies with the policy, the issue is automatically removed from the active list. No manual resolution steps are needed.
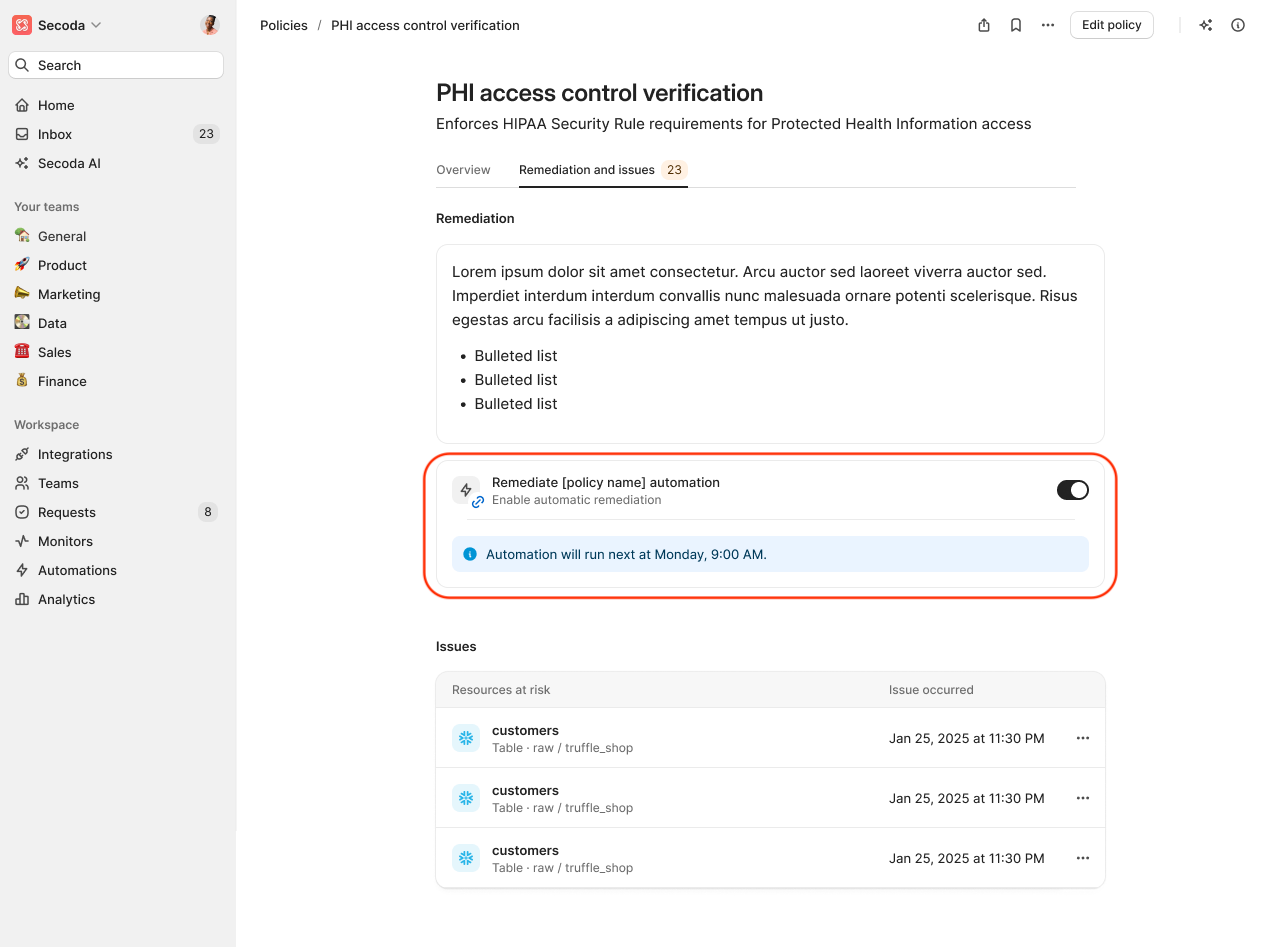
Automations with Policies
Automations in Secoda allow you to automatically remediate policy issues by updating metadata directly when certain conditions are met. When a policy is tied to metadata—such as classification, owner, or retention period—you can use automations to bring non-compliant resources back into alignment without manual intervention.
When a policy is associated with structured metadata—such as classifications, owners, or descriptions—Secoda allows you to create an automation directly from the policy screen. This helps streamline setup by pre-filling relevant conditions and actions based on the policy definition.
Policy Page
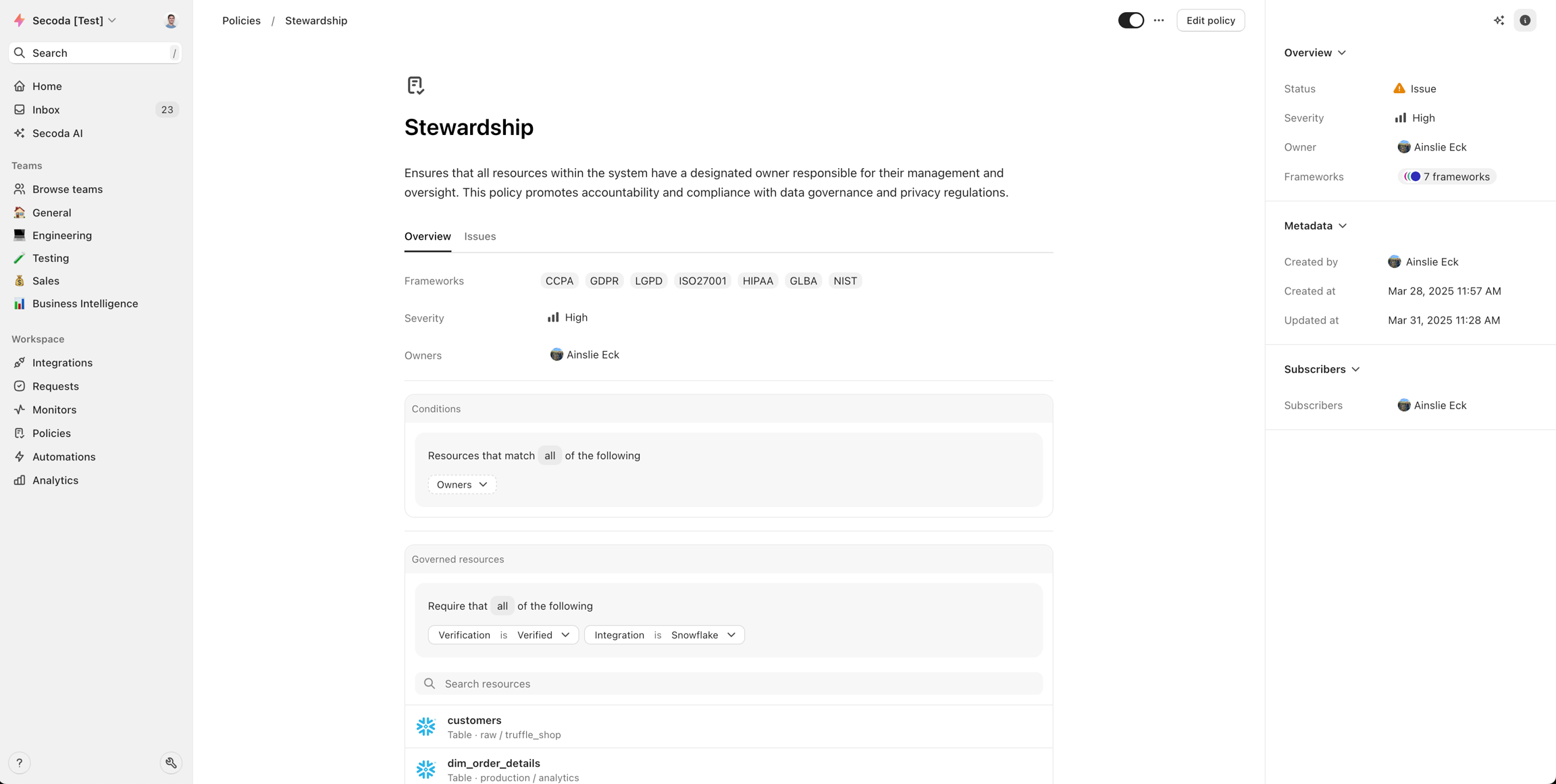
Overview Tab
The overview tab contains the primary policy configuration and details:
Description
Frameworks
Severity (Low, Medium, High)
Governed resources
Policy conditions
Issues Tab
Monitor and manage policy violations:
View current policy violations
Remediation steps
Manage issue resolution
Last updated
Was this helpful?