Snowflake
An overview of the Snowflake integration with Secoda
Snowflake Metadata Extracted
Getting Started with Snowflake
Step 1: Create Role for Secoda
CREATE ROLE SECODA;
GRANT imported privileges on database SNOWFLAKE to ROLE SECODA;
GRANT USAGE ON WAREHOUSE "<warehouse>" TO ROLE SECODA;
// ====== Existing Tables & Schemas
begin;
set database_name = <database name>;
// Usage on database object
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE identifier($database_name) TO ROLE SECODA;
// Usage on existing schemas
GRANT USAGE,MONITOR ON ALL SCHEMAS IN DATABASE identifier($database_name) TO ROLE SECODA;
// References for INFORMATION_SCHEMA to existing tables
GRANT SELECT ON ALL TABLES IN DATABASE identifier($database_name) TO ROLE SECODA;
GRANT SELECT ON ALL VIEWS IN DATABASE identifier($database_name) TO ROLE SECODA;
// ====== Future Tables & Schemas
// Read access to all schemas created in the future (but not current ones)
GRANT USAGE,MONITOR ON FUTURE SCHEMAS IN DATABASE identifier($database_name) TO ROLE SECODA;
// Reference for INFORMATION_SCHEMA to all tables created in the future (but not current ones)
GRANT SELECT ON FUTURE TABLES IN DATABASE identifier($database_name) TO ROLE SECODA;
commit;Step 2: Create User for Secoda
Key-Pair Authentication
Step 3: Whitelist Secoda IP Addresses
Step 4: Connect Snowflake to Secoda
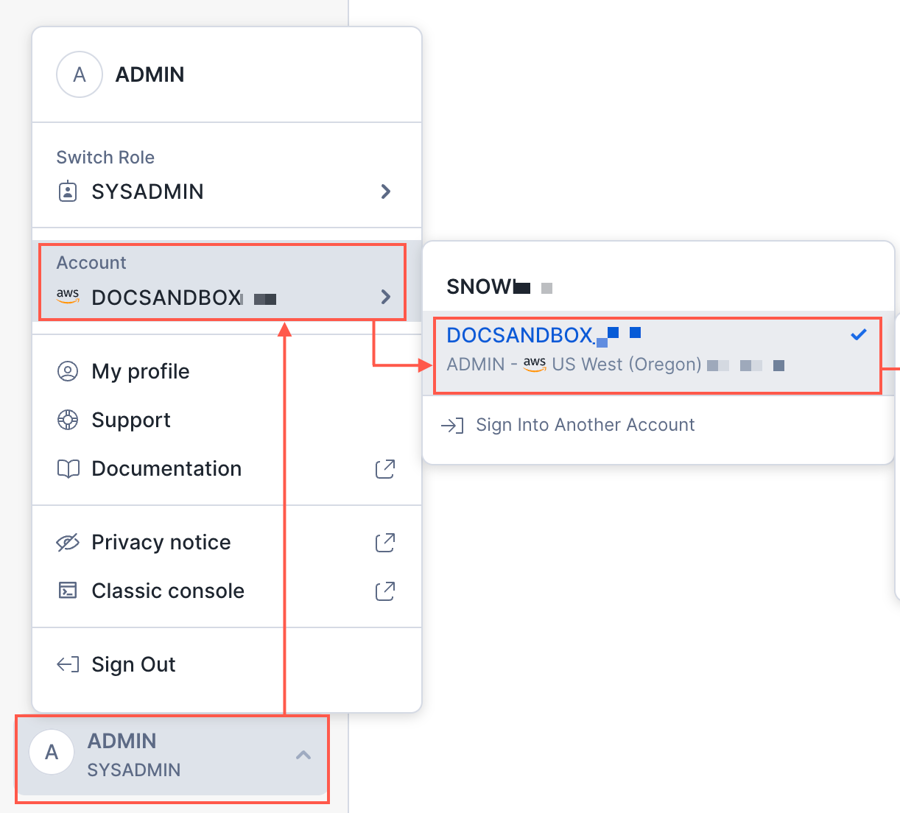
How do I find my Account ID?
Troubleshooting
Account ID is not part of URL
Account usage not authorized
Could not connect to Snowflake backend after 0 attempt(s)
Missing schemas
Last updated
Was this helpful?